


|



| 产地 | 广州 |
| 品牌 | 现货 |
| 货号 | JL1136 |
| 保存条件 | 4-30度 |
| CAS编号 | |
| 保质期 | 2年 |
mob:13802525278 杨qq:506563099 小郑在线
单项违禁品尿液检测板-违禁品单卡检测试剂
广州健仑生物科技有限公司
广州健仑生物科技有限公司长期供应:尼古丁检测试剂盒,可替宁检测试剂盒,违禁品检测试剂盒
我司同时提供独立包装试剂盒:bzo-bar-coc--thc -met--opi-oxy-mdma-*- amp-xtc-mtd 或联检试剂盒(胶体金法)
检测范围:*、KET、mamp、MDMA、BZO、THC、*、MTD、BAR、MDMA、AMP、BUP、PCP、TCA、OXY、MET等等。
产品特点:可以根据需求自主订制多联卡。多联卡自由组合,从二联到十五联都可以订制。单项违禁品尿液检测板-违禁品单卡检测试剂
产品规格:40t/盒
有效期:2年
保存温度:4-30度
测试前让测试条,尿液样本和/或对照物达到室温(15-30°C)。
1.打开袋子之前将袋子放到室温。 从密封袋中取出试纸并尽快使用。
用箭头指向尿液样本,浸入测试条
2.在尿样中至少10-15秒。 浸泡条时,不要通过测试条上的*线(MAX)。 见下图。
3.将测试条放在不吸水的平面上,启动定时器,等待出现彩色线条。 结果应在5分钟后读取。 10分钟后不要解释结果。
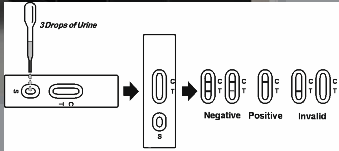
负面:*显示两行。 一条彩色线应该在控制区域(C),另一条明显的彩色线应该在测试区域(T)。 该阴性结果表明*浓度低于可检测水平(1,000 ng / mL)。
*注意:测试线区域(T)的颜色阴影会有所不同,但是每当有微弱的线条时,总是应该将其视为负值。
正面:控制区域(C)出现一条彩色线条。 测试区域(T)不出现任何线条。 该阳性结果表明*浓度超过可检测水平(1,000 ng / mL)。
无效:控制线无法显示。 标本体积不足或不正确的程序技术是控制线失败的最可能的原因。 检查程序并使用新的测试条重复测试。 如果问题仍然存在,请立即停止使用该批次,并联系您当地的经销商。
我司还提供其它进口或国产试剂盒:登革热、疟疾、流感、A链球菌、合胞病毒、腮病毒、乙脑、寨卡、黄热病、基孔肯雅热、克锥虫病、违禁品滥用、肺炎球菌、军团菌、化妆品检测、食品安全检测等试剂盒以及日本生研细菌分型诊断血清、德国SiFin诊断血清、丹麦SSI诊断血清等产品欢迎致电。

微信二维码扫一扫

【公司名称】 广州健仑生物科技有限公司
杨永汉
【公司
【腾讯 qq 】 506563099 小郑
【公司网址】 www.jianlun。。com
【公司地址】 广州清华科技园创新基地番禺石楼镇创启路63号二期2幢101-103室



The first is secreted by 84 amino acid long-chain polypeptide - Proinsulin (proinsulin), through the role of specific proteases - proinsulin converting enzyme (PC1 and PC2) and carboxypeptide quinone E, will be the middle part of proinsulin ( The C chain) is cleaved, and the carboxy-terminal portion (A-chain) and the amino-terminal portion (B-chain) of proinsulin are bound together by disulfide bonds to form insulin.
Mature insulin is stored in secretory vesicles in the pancreatic beta cells and exists as a hexamer coordinated with zinc ions. Under external stimulation, insulin is released into the blood with the secretory vesicles and exerts its physiological effects.
Insulin secretion is divided into two parts, one part is to help maintain normal fasting blood glucose and secrete insulin, called basal insulin, and the other is to lower postprandial blood glucose and maintain normal postprandial blood glucose secretion of insulin, known as mealtime insulin. . Premature insulin secretion during mealtime controls the magnitude and duration of postprandial hyperglycemia. Its main effect is to inhibit the production of endogenous glucose in the liver. Through this mechanism of action, blood glucose is controlled at levels close to the fasting state at any time; postprandial blood glucose peaks below 7.0 mmol/L, and blood glucose levels above 5.5 mmol/L do not exceed 30 minutes. Before diagnosis of diabetes in patients with type 1 diabetes, autoimmune destruction of pancreatic islet β cells occurs in most patients, leading to a reduction in both mealtime and basal insulin secretion. The abnormal progression of pancreatic β-cell function in type 2 diabetes patients is slow, and often manifests as peripheral insulin resistance, but there is also a decrease in insulin-phase secretion, which can lead to normal fasting blood glucose and increased postprandial blood glucose. Ultimately, postprandial blood glucose levels can reach four times that of non-diabetic physiological conditions, and blood glucose rises after meals for several hours, so that it is still significantly elevated before the next meal. The insulin preparations that compensate for insufficient insulin secretion at the time of the meal include Novo Ling R and insulin analog preparations such as Nuohe Rui.